#Day7 Task: Understanding package manager and systemctl
#Day7 of 90DaysofDevOps
Table of contents
- What is a package manager in Linux?
- What is a package?
- Different kinds of package managers?
- Install docker and Jenkins in your system from your terminal using package managers. ?
- Installing Docker
- Installing Jenkins
- Step 1 – Installing Java Development Kit
- Write a small blog or article to install these tools using package managers on Ubuntu and CentOS.
- Note on systemctl and system?
What is a package manager in Linux?
In simpler words, a package manager is a tool that allows users to install, remove, upgrade, configure and manage software packages on an operating system. The package manager can be a graphical application like a software center or a command lines tool like apt-get or Pacman.
What is a package?
A package is usually referred to as an application but it could be a GUI application, command line tool or a software library (required by other software programs). A package is essentially an archive file containing the binary executable, configuration file and sometimes information about the dependencies.
Different kinds of package managers?
Package Managers differ based on the packaging system but the same packaging system may have more than one package manager.
For example, RPM has Yum and DNF, package managers. For DEB, you have apt-get, aptitude command line-based package managers.
Install docker and Jenkins in your system from your terminal using package managers. ?
Installing Docker
First, update your existing list of packages:
sudo apt update
Next, install a few prerequisite packages which let apt use packages over HTTPS:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
Then add the GPG key for the official Docker repository to your system
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Add the Docker repository to APT sources:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal stable"
This will also update our package database with the Docker packages from the newly added repo.
Make sure you are about to install from the Docker repo instead of the default Ubuntu repo:
apt-cache policy docker-ce
You’ll see output like this, although the version number for Docker may be different:
docker-ce:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 5:19.03.9~3-0~ubuntu-focal
Version table:
5:19.03.9~3-0~ubuntu-focal 500
500 https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal/stable amd64 Packages
Notice that docker-ce is not installed, but the candidate for installation is from the Docker repository for Ubuntu 20.04 (focal).
Finally, install Docker:
sudo apt install docker-ce
Docker should now be installed, the daemon started, and the process enabled to start on boot. Check that it’s running:
sudo systemctl status docker
The output should be similar to the following, showing that the service is active and running:
Output
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-05-19 17:00:41 UTC; 17s ago
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 24321 (dockerd)
Tasks: 8
Memory: 46.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─24321 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Installing Jenkins
Step 1 – Installing Java Development Kit
Jenkins requires the Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk
java -version
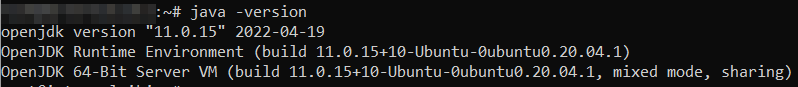
It is recommended to install Jenkins using the project-maintained repository, rather than from the default Ubuntu repository. The reason for that is that the Jenkins version in the default Ubuntu repository might not be the latest available version, which means it could lack the latest features and bug fixes.
Add the Jenkins repository key: To ensure that the Jenkins package comes from a trusted source, add the Jenkins repository key to your system with the following command.
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key |sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins.gpg
Add the Jenkins repository to your system:
sudo sh -c 'echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins.gpg] http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
Update your package manager's cache:
sudo apt update
Finally, install Jenkins:
sudo apt install jenkins
After installation, start the Jenkins service and check the status:
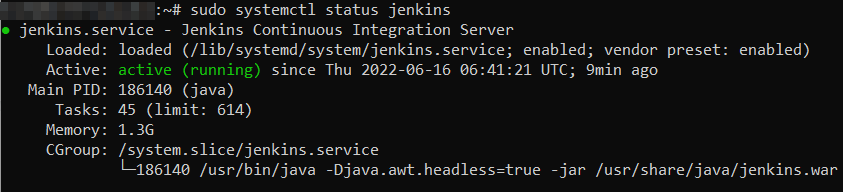
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl status jenkins
Opening the Firewall
sudo ufw allow 8080
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw status
Write a small blog or article to install these tools using package managers on Ubuntu and CentOS.
If you're looking to install tools like Docker and Jenkins on your Ubuntu or CentOS machine, you'll be happy to know that it can be done quickly and easily using your package manager. Package managers are designed to simplify the installation process for software and libraries by handling dependencies and other installation tasks automatically. In this article, we'll cover how to install Docker and Jenkins using package managers on Ubuntu and CentOS.
Installing Docker on Ubuntu and CentOS
Docker is a containerization platform that allows you to create and run applications in containers. Installing Docker on Ubuntu and CentOS is a straightforward process that can be done using the package manager. Follow the steps below to install Docker on Ubuntu and CentOS.
Ubuntu:
1 Open your terminal and update your package list by typing the following command:
sudo apt-get update
2 Once the package list is updated, install Docker by running the following command:
sudo apt-get install docker.io
3 After Docker is installed, start the Docker service using the following command:
sudo systemctl start docker
4 Finally, enable Docker to start on boot by running the following command:
sudo systemctl enable docker
CentOS:
Open your terminal and update your package list by typing the following command:
sudo yum update
2 Once the package list is updated, install Docker by running the following command:
sudo yum install docker
3 After Docker is installed, start the Docker service using the following command:
sudo systemctl start docker
4 Finally, enable Docker to start on boot by running the following command:
sudo systemctl enable docker
Installing Jenkins on Ubuntu and CentOS
Jenkins is a popular open-source automation server that can be used to automate various tasks related to building, testing, and deploying software. Follow the steps below to install Jenkins on Ubuntu and CentOS.
Ubuntu:
Open your terminal and add the Jenkins repository key to your system using the following command:
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
2 Next, add the Jenkins repository to your system by running the following command:
sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
3 Once the repository is added, update your package list by typing the following command:
sudo apt-get update
4 Finally, install Jenkins using the following command:
sudo apt-get install jenkins
CentOS:
Open your terminal and add the Jenkins repository to your system using the following command:
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo
Next, add the Jenkins repository key to your system by running the following command:
sudo rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key
3 Once the repository is added, update your package list by typing the following command:
sudo yum update
4 Finally, install Jenkins using the following command:
sudo yum install jenkins
Conclusion
Using package managers to install tools like Docker and Jenkins on Ubuntu and CentOS can save you a lot of time and effort. Package managers take care of dependencies and other installation tasks, making the process much simpler and faster. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can quickly and easily install Docker and Jenkins on your Ubuntu or CentOS machine.
Note on systemctl and system?
systemctl is a command used to manage system services and units in Linux, while system is a directory in the root file system that contains important system configuration files.
